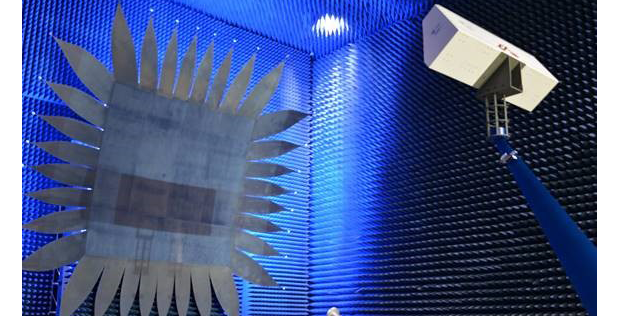
Darpa has announced a sensor system developed under the Arrays at Commercial Timescales – Integration and Validation (ACT-IV) program.
Northrop Grumman, the primary research team on the ACT-IV program, facilitated the transition of the advanced digital active electronically scanned array (AESA) to the Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Dayton, OH.
ACT-IV is a multifunction AESA system that is capable of simultaneously performing different operations, such as radar, electronic warfare (EW), and communications functions, at different modes, says Darpa.
At the system’s core is an advanced semiconductor device – or common module – fabricated in commercial silicon that was originally developed by Darpa’s Arrays at Commercial Timescales (ACT) program.
At the Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, the ACT-IV system will become a Department of Defense (DoD)-wide asset for testing and experimentation with new modes of radar, communications, sensing, and EW. The software, algorithms, and capabilities developed on the program will also transition to next-generation multifunction RF systems to support advanced defense development programs and a future open-architecture environment.
[Image courtesy: Air Force Research Laboratory]